Month: October 2023
How to Stop Tree Roots From Growing Back
Removing tree roots is just as important as cutting down the trunk. You might be wrong if you think your job is done after you’ve cut down the tree and removed its stump.
The roots underneath will continue growing if you don’t remove them. Skip the risk of dealing with overgrown tree roots by taking the necessary actions that ensure complete elimination.
Let us walk you through this guide and learn how to stop tree roots from growing back and why seeking an expert arborist’s help is your best option.
Will Roots Keep Growing After Cutting the Tree?
Many believe cutting down a tree will also stop its roots from growing. This common misconception is far from the truth.
A tree’s roots may continue to grow and spread through the soil after cutting it down. This allows the tree to reappear from the stump or produce new shoots from the roots.
Various factors, including the type of tree, the soil, and the environment, can affect how far the roots spread. Sometimes, roots can keep growing for years or even decades, ruining your landscape.
Understanding how to stop tree roots from growing back and prevent future damage to the home’s structure is vital.
Why Root Removal Matters
Overgrown roots pose several threats to your landscape. Since these bothersome remnants can and will continue to develop even if the tree is no longer standing, tree root removal becomes necessary.
Roots remaining in the ground after tree removal can cause a variety of issues, including:
- Structural Damage – Tree roots can penetrate and grow underneath foundations, sidewalks, and utility lines, resulting in expensive property damage.
- Interference with New Landscape – Existing roots can interfere with your plans to create a new landscape design for that particular area in your property.
- Unwanted Tree Regrowth – As previously stated, roots can produce new branches, regrowing undesirable trees or shrubs.
Avoiding these issues requires complete tree and root removal to ensure structural safety within your property.
Ask the Experts: How to Stop Tree Roots from Growing Back
Even with the best techniques, removing tree roots might take a long time. You have to be patient and willing to apply various methods if one strategy fails to do the job. But remember to refrain from using these techniques at the same time.
Now that you know why tree root removal is important, let’s look at some techniques for keeping tree roots from sprouting back following tree removal.
Preparing for Root Removal
The most common and dependable way of removing tree roots involves using a chainsaw to chop down the tree stump. Some also use a reciprocating saw to cut huge roots if necessary.
Knowing how to utilise these instruments properly is essential to reduce the risk of injury. For starters, wear proper attire, such as a long-sleeved shirt and full-length slacks.
Wear gloves and goggles to safeguard your hands and face from flying debris. Check your worksite for any obstructions that could cause delay and damage your machine or put you in danger, such as excessive dirt, large and small pebbles or other unnecessary objects.
DIY Remedy
Start removing the tree root with softer materials before applying more heavy-duty methods.
Salt and boiling water are nearly as effective as chemical herbicides and root killers without the side effects of destroying surrounding plants. These solutions are also highly cost-effective, preventing you from spending much on the process.
However, it’s important to know that these techniques may take longer. Hence, if you want a quick result, you may apply chemical herbicides and move on to the next step.
Epsom or Rock Salt
- Drill some holes with a depth of 7.6 to 10.1 cm to remove the stump and roots. You will also need to drill holes into the large surface roots.
- Fill the holes with salt. Ensure it does not overflow, especially if there are neighbouring plants.
- Repeat the second step every few months until each root is dead. When the roots become hollow and withered, and no new sprouts are present on or around the trunk, the roots have stopped growing.
Boiling Water
- Dig up and reveal as many roots as you can.
- Cut the stump closer to the roots with a chainsaw.
- Drill holes with a depth of 7.6 to 10.1 cm into the stump and the overgrown roots sprawling from the ground.
- Ensure to cover as many roots as possible when you pour boiling water. It can swiftly damage and shock the roots, although the results may not immediately be visible. If necessary, repeat the process after a few days.
Vinegar
- Dig up and uncover as many roots as you can with a shovel.
- Eliminate the existing stump and overgrown roots by drilling holes into them and filling the gaps with vinegar.
- Spray vinegar into the remaining stump once you see leaves or sprouts growing.
- Repeat the second step every month until the roots are dead. Try a different technique if there are no changes made after months.
Digging the Root Out
You will need to gather the following equipment to remove smaller roots in your lawn or those remaining ones from prior methods:
- Drill
- Shovel
- Hatchet or Reciprocating Saw
- Garden hoe
Remove the soil from the remaining tree trunk and roots for easier removal. Apply homemade remedies, store-bought root killers, or herbicides to weaken the roots, making them more manageable after a few weeks.
For overgrown roots, utilise a reciprocating saw with proper safety precautions or, if you prefer, a hatchet, but it may take more effort.
Alternate right and left strikes with the hatchet to make a V-shaped cut. Ensure to take pauses when you feel tired to avoid injuries and accidents.
Start from the farthest point and work inwards when dealing with an overgrown root to ensure safety. After removing the major roots, dig and uncover the remaining smaller roots using a garden hoe or shovel.
Using Chemical Herbicides
Chemical herbicides are a promising option for prompt tree root removal. You can buy one in stores, but always read the label and confirm the necessary contents.
Prioritising safety when utilising chemical herbicides is critical. Wearing protective gloves and full-length clothing is essential to avoid direct contact with the chemical, as it can harm more than just plants. Choose clothes that you can directly dispose of after use.
Moreover, keeping children, pets, or anyone out of the work area until it is safe and the herbicide completely dries is a must. Remember to change your clothes and thoroughly wash your hands after completing the task.
Top Reasons to Get Rid of Old Tree Roots
Tree roots in your landscape can cause several problems, including soil disturbance, slope erosion, damage to concrete roads and walks, sewer lines, drains, and other infrastructure. It is even more concerning once the roots start to cause harm to your neighbours’ property.
Additionally, pests such as mice, rats, and termites might plague old tree stumps or roots, causing severe damage and infestation to your home.
Although you can solve the problem yourself, DIY remedies take time and effort. Hence, your best option is to hire a professional arborist to remove roots from sewer lines, pipelines, and drains, minimising any risks of dealing with these delicate structures.
Seek a Professional
When DIY tree root removal becomes too tough to handle due to it being laborious and time-consuming, seeking the experts’ help is your best way out.
You don’t need to spend all your time waiting for weeks or months to stop tree roots from growing back in your yard. We at Trees Down Under are the professional arborists you need to deal with extensive root systems and stubborn tree roots.
We can eliminate all your uncertainties about the proper tree removal methods. Our professional arborists have the expertise and equipment required to safely and efficiently remove tree roots.
Our team minimises your property’s potential damages through our effective and hassle-free root removal service.
Remember that Trees Down Under is your best choice when addressing tree roots. Contact us today for enquiries and bookings!
Horticulture Statistics Australia (2023)
Australia’s horticulture industry continuously booms, significantly contributing to the country’s economy. It is critical to produce healthy and fresh products, such as fruits, nuts and vegetables, domestically and globally.
According to the recent data released by Hort Innovation, the value of Australia’s horticulture industry has rocketed to A$6.15bn in the last decade.
The Horticulture Statistics Handbook’s latest edition, crafted by Freshlogic on behalf of Hort Innovation, includes this new information and data on 75 various horticulture categories, such as fruits, nuts, vegetables, and green life.
Let us delve into Australia’s horticulture statistics and get a significant glimpse of various records and facts about producing fruits, vegetables, nuts and other crops.
Such information can help us understand how the horticulture industry affects the country and its people in various ways.
Australian Horticulture Industry Stats and Facts
The Australian horticulture industry expects its production gross value to increase to $17.6 billion by 2023-24. Higher production also means a rise in exports by 9% to $3.7 billion.
These significant forecasts urge the industry to strive more despite drier weather conditions. The projected onset of El Niño in 2023-24 may result in drier conditions over Australia, especially in Eastern Australia.
Drier weather may increase water prices. However, historically, the currently observed low water prices and high water storage levels will likely lessen the impact on water costs.
According to ABARES’ latest Water Market Outlook, average water allocation costs are predicted to continue far below recent highs under the likely average scenario. Low water prices will continue to benefit horticulture production.
Moreover, labour availability improvements and higher expected demand from foreign markets drive the increase in production volumes throughout 2023-24.
The country’s horticulture industry is a lively and essential aspect of its agricultural sector. It includes a wide variety of crops, significantly contributing to the volume and value of production.
Knowing Australia’s fruits, nuts, and vegetable statistics for 2023, which are essential figures and facts of the horticultural industry, allows us to be aware of such important information.
Here’s a closer look at horticulture statistics in Australia for more insights:
Fruits
Australia has a diverse range of fruits cultivated across the country. According to the Horticulture Statistics Handbook 2021/22, total fruit production of 307,630t is valued at $5,521.9M in the year ending June 2022.
- In 2021-22, Australia exported 3,141 tonnes of apples.
- Mango volumes rose to 10% over the previous year, resulting in the highest production value of $217.9M.
- Australia’s total avocado production was 122,197t worth $363.8M, with an importation of 12,640 tonnes and exportation of 11,611 tonnes.
- Total banana production ending June 202 was 374,033t and valued at $501.6M
- For the past years, the berry sector, including blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, has rapidly expanded.
- 55% of Australian homes purchased blueberries, with an average of 160g bought every shopping trip.
- Fresh strawberries’ production of 68,311t was valued at $416.8M in the year ending June 2022.
- From 2021–2022, the value of several fruit categories significantly increased, including nectarines/peaches ($8M), watermelons ($27M), mangoes ($17M), mandarins ($14M), lychees ($10M), and table grapes ($90M).
Nuts
Australia is also well-known for producing high-quality nuts, especially almonds and macadamias. The following are some significant figures from the nut industry:
- Total nut production in 2021-22 was 287,079t (in-shell) and 176,993t (kernel) valued at $1,387.5M
- The cracking process caters to 65% of nut production (in shell)
- Chestnut sales accounted for 16% of all Australian household purchases, with 290g being the average amount per shopping trip.
- Australia is the world’s second-largest producer of almonds, with production reaching 1 205,436t (in-shell) and 143,805t (kernel) worth $916M.
- The country accounts for around 30% of the world’s supply of macadamia nuts, making it the largest producer globally. Australia exported 11,426 tonnes of macadamias in shell and 9,941 tonnes of macadamia kernel in 2021-22.
- Australia imports hazelnuts, with the majority being in kernel form. The country is a net importer of this variety of nuts, importing 3,170 tonnes of kernel hazelnuts while exporting 1 tonne each of kernel and in-shell hazelnuts.
Vegetables
Vegetable farming is one of the most significant horticulture sectors in Australia. It is diverse and productive, with a yearly production of 3.4 million tonnes worth 2.2 billion dollars.
New South Wales (NSW) grows 15% of all Australian produce, supplying the fresh and processing markets. 60% of vegetables produced in Australia are grown for the fresh market and sold domestically.
There are two major research centres established by the NSW Department of Primary Industries (DPI) focusing on vegetable research.
These facilities are The National Vegetable Industry Centre at Yanco Agricultural Institute in the Riverina and the National Centre for Greenhouse Horticulture on the central coast at Gosford Horticultural Institute.
The NSW DPI workers take initiatives in exploring pest and disease management, comprehensive pest management, irrigation, and variety evaluation.
Here are some relevant figures and information on vegetable horticulture in Australia:
- Despite a slight drop in output from the previous year, vegetable production values hit an all-time high of $5.54B in 2021/22.
- Australia widely cultivates potatoes, making them one of the most extensively grown vegetables in the country, with over 1,462,065t produced in 2021/22.
- In 2021-22, Australia produced around 436,907t of tomatoes worth $645.1M
- Beans had the largest yearly production value growth rate of any vegetable, increasing 64% in 2021/22 and reaching a high of $134.4M.
- Bean purchases comprised 44% of household spending in Australia, with each store trip averaging 509g.
- Onions’ production value of onions hit $249M, setting new records.
- Total asparagus production was 7,368t valued at $77.9M.
- Australia imports more broccoli and cauliflower than exports. In 2021-201, Australia exported 1,873 tonnes of these vegetables.
- Another significant vegetable crop in Australia is the carrot, with production reaching 306,394t valued at $247.9M in 2021/22.
- There are three primary farming systems used to produce cucumbers in Australia. These systems and their contributions to production are conventional – 44%, poly houses and tunnels – 42% and glasshouses – 14%.
- Production volumes of leafy salad vegetables increased by 5.3 per cent in 2021/22. This was the most abundant year for fresh green salad veggies.
- The vegetable category had value gains across the board, with leafy salad vegetables increasing by 19% (+$94.2M) and tomatoes rising by 15% (+$83M).
Other Horticulture Areas
Aside from fruits, nuts, and vegetables, the Australian horticulture industry includes other fields contributing to the country’s agricultural diversity and economic prosperity.
Let us look into some relevant data and facts concerning other horticultural areas in Australia:
- The production value of other horticulture areas was $3.45B
- The fresh supply’s wholesale value was $3.71 billion.
- Australia’s cut flower and decorative plant sector, which serves domestic and foreign markets, is estimated to be worth $740 million.
- In 2021/22, Australia’s cut flowers importation was worth $104.6 million, with $9.5 million in exports.
In 2021-22, a reduction of some fresh fruits and vegetables supply due to severe floods in Queensland and New South Wales’s major horticultural regions led to increased domestic prices.
However, the flooding’s impact on production has reduced, resulting in moderated price growth.
According to quarterly figures for June 2023, year-end fruit and vegetable inflation is at 1.6%. This figure roughly matches the 1.4% average quarterly inflation growth of the pre-pandemic year-end.
A review of the Horticulture Statistics Handbook conducted in 2012/13 demonstrates growth in both horticulture production volumes and values.
In 2023-24, there is a projected increase in the global demand for horticulture goods. However, it is also expected that global supply growth will outstrip it.
Increasing populations and real incomes in some emerging economies will promote demand growth. Yet, persistently high inflation in many developed nations will weigh on consumer real incomes, partially offsetting this increase.
Summary
The Australian horticulture industry plays a major role in the overall productivity and prosperity of the country. It significantly showcased Australia’s capacity to produce premium fruits, nuts, vegetables and other horticultural goods.
As we’ve learned about the relevant horticulture statistics in Australia, it is clear that this industry supports the economy and provides fresh and nutritious produce to the entire population.
The industry has defied many odds to achieve an upswing in value and is now ready to welcome significant growth in the years ahead.
With the support and collaboration of the government, related organisations, industries, investors, producers and consumers, Australia’s horticultural sector can go a long way in reaching its projected production and value.
Deforestation Statistics Australia (2023)
Amidst its captivating landscapes and unique biodiversity, Australia faces a concerning battle against deforestation.
According to records, the continent ranked first for mammal extinctions globally and second for biodiversity loss, damaging an average of 416,840 hectares of forestry yearly. It’s surprising that only Australia is on this list among other developed nations.
Australian trees’ deforestation and wildlife extinctions are not just a concern of one country but a global catastrophe needing relevant actions. Let us look into the latest deforestation statistics in Australia to get a significant glimpse of this phenomenon.
Drivers of Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal or clearing of trees or forests in a particular land area due to various complex factors that interplay with one another. These factors are both natural and man-made, requiring mitigating actions to reduce the adverse impacts.
Here are some of the main drivers of Australian trees’ deforestation:
1. Population Growth
As the population grows, so does the need for various infrastructures, housing and agriculture to cope with the needs of the people.
Forests often suffer from this situation as many of these areas undergo significant development and conversion to cater to the increasing population.
2. Logging and Timber Production
The logging and timber industry requires cutting down trees to produce wood and other products, including paper, furniture and construction materials. Unsustainable and irresponsible logging practices may reduce forest resources.
3. Agricultural Expansion
Another common driver of deforestation is the conversion of forests into agricultural land. This circumstance does not only happen in Australia but globally.
The growing human population’s increasing demands for food supply led to land clearing for crop cultivation and livestock production.
4. Infrastructure Development
Various infrastructure developments, such as the construction of highways, roads, buildings and urban areas, often require forest clearing, leading to significant deforestation.
These expansions can destroy forest ecosystems, causing them to be more susceptible to loss and deterioration.
5. Fire
Deforestation may also result from natural or human-induced fires. People or developers may conduct land clearance by intentionally setting the forests on fire as a means of land management.
On the other hand, natural forest fires or wildfires are often brought and intensified by climate change, leading to extensive deforestation.
6. Climate Change
Increasing temperatures and altered weather patterns due to climate change affect forests’ conditions, making them more vulnerable to pest infestations and diseases.
This indirect impact often prompts management practices to cut down trees in the affected areas to mitigate the damages, contributing to deforestation.
7. Mining and Extraction
The presence of mining industries also leads to significant forest clearing. Oil, coal and mineral extraction are just a few of these activities that can destroy wildlife habitats and cause water pollution and soil erosion.
8. Illegal Logging
Unlawful practices such as illegal logging are also one significant driver of deforestation. Such activities threaten the forest resources and cause crime and corruption.
9. Inadequate Policy Awareness and Enforcement
Combating deforestation requires intensive implementation of laws and dissemination relevant information for awareness. The lack or weak enforcement of protective rules and regulations may intensify deforestation.
The governing bodies need to impose consequences for illegal land clearing and logging to reduce the adverse impacts on the forest lands.
Deforestation Statistics Effects and Facts
Have you ever wondered how many trees are cut down annually in Australia?
Australia has lost much of its forests for the past two centuries. The Global Forest Watch reports in 2019 showed Australia has lost 800,000 hectares of tree cover. It was the country’s second-highest annual loss recorded in history.
The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) also revealed that the country holds one of the developed nations’ highest deforestation rates. Since European settlement, around 40% of Australia’s woodlands and forests have been destroyed.
Every 86 seconds, Australia suffers the destruction of forest areas equivalent to Melbourne Cricket Ground (MCG), which is very concerning.
Environmental Impact of Deforestation
Massively removing forests and trees from a region has significant and far-reaching environmental impacts.
Not only do these consequences affect the nearby ecosystems, but they also add to global environmental problems. Let us take a closer look at how deforestation affects the environment:
Loss of Biodiversity
Australia provides shelter to diverse species, and forests are a critical part of their habitat. The increasing rate of deforestation disturbs ecosystems, causing habitat loss and destruction.
According to the WWF, deforestation endangers over 1,000 plant and animal species in Australia.
Since 1750, Australia has lost 28% of its mallee forest, 27% of its rainforest, 19% of its open forest, and 11% of its woodland forest. Only half of Australia’s forests and bushlands have survived since the pre-European arrival.
On the other hand, similar to most regions in the world experiencing deforestation, agricultural production is primarily to blame. The increasing demands of consumers for various commodities spark the development of farmlands in forest areas.
Based on a 2022 Queensland Conservation Council and Wilderness Society report, over three-quarters of the 2.1 million hectares of forested vegetation were destroyed between 2014 and 2019 on cattle-producing lands.
Australia’s supply chains with the highest risk of deforestation are under pressure to adopt sustainable practices. Such actions are necessary to address the growing consumer demand for commodities produced without causing deforestation.
Tree Cover Loss
- Between 2001 and 2022, Australia suffered from 8.85 Mha tree cover loss, which is a counterpart of a 21% decline from 2000 and 2.30 Gt of CO2e emissions.
- Deforestation resulted from most tree cover loss in Australia between 2001 and 2022, accounting for 2.2% of the total degradation.
- New South Wales and Western Australia are the top two regions in Australia responsible for 59% of total tree cover loss between 2001 and 2022.
- New South Wales had the greatest tree cover loss at 3.01 Mha, while Western Australia had 2.24 Mha.
- Australia had a tree cover change of -917 kha (-1.0%) between 2000 and 2020.
- Between 2000 and 2020, Australia increased its tree cover by 1.60 Mha or 1.2% of the global total.
Mammal Extinctions
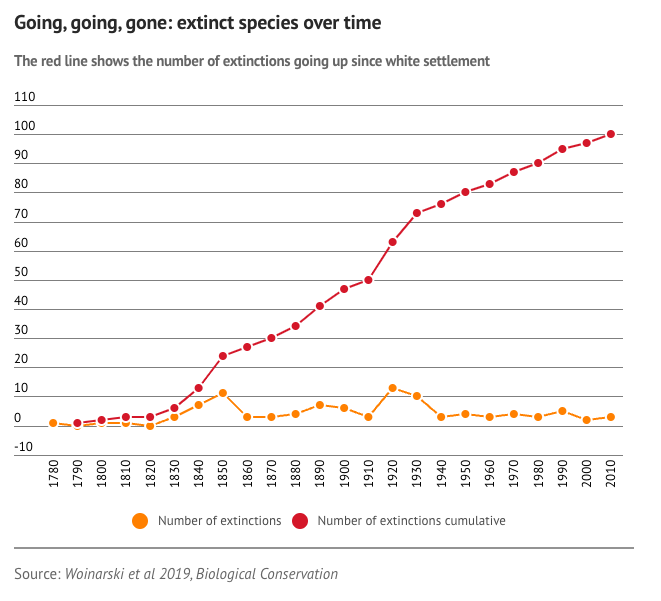
- Australia has had the highest number of mammal extinctions worldwide.
- In Australia, 37 plant and 55 animal species had perished as of this writing.
- In Queensland and New South Wales, habitat loss mainly threatens the presence of koalas.
- Between 2019 and 2020, there was land clearing activity in Queensland totalling 147,575 ha to rear cattle for meat inside mapped areas that are known and expected to be koala habitats.
Carbon Emissions
Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are one of deforestation’s most crucial environmental impacts. Trees absorb CO2 during photosynthesis, serving as carbon sinks.
Burning or destroying trees leads to emissions of the stored carbon into the environment. According to the Australian Academy of Science, deforestation accounts for about 8% of the country’s greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, land clearing in Australia results in carbon emissions that are nearly one-third of all emissions produced by coal-fired power plants in the entire country.
If native forest logging emissions are considered, the percentage equals at least half of the carbon pollution produced by all Australian coal-fired power plants.
Efforts to Combat Deforestation
An integrated strategy involving sustainable land management practices, government regulations, ethical consumer behaviour, and international collaboration is necessary to battle deforestation.
Combating deforestation focuses on upholding sustainable forestry, safeguarding high-conservation-value forests, and tree replanting activities to replace lost forest cover.
Additionally, it is crucial to deal with the underlying causes of these worldwide environmental problems in order to find the best long-term solutions:
Forest Certification
Consumers may easily recognise wood supplies from sustainably managed forests thanks to certification organisations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), promoting ethical logging methods.
Indigenous Lands Management
The forests’ preservation and sustainable practices promotion can benefit greatly from working with Indigenous communities with in-depth land management expertise.
Global Collaboration
Australia collaborates globally to stop deforestation, understanding that such a phenomenon is a significant problem that crosses international boundaries.
The country aims to maintain its distinctive ecosystems while contributing to global efforts to battle deforestation through collaborative efforts between governments and international organisations.
With this, all participating countries can build more resilient and sustainable futures and environments.
Conservation Initiatives
Australia has adopted several conservation programs and legislation, such as the “National Landcare Program”, which promotes sustainable land management techniques.
The “20 Million Trees Program” is part of the National Landcare Program of the Australian Government, aiming to develop healthy, self-sufficient tree-based ecosystems across the country by planting 20 million native trees and understory.
Tree care and clearing companies in Australia also adhere to preservation standards and regulations set by the authorities for environmental protection.
Summary
Australia’s deforestation is a crucial issue threatening the country’s biodiversity and unique ecosystems. It also significantly contributes to worldwide climate change.
Knowing and monitoring deforestation statistics in Australia is essential for the continued implementation of various initiatives to combat such a serious issue.
Moreover, the presented deforestation statistics in Australia showed the importance of tackling deforestation urgently and effectively.
We must understand that the trees’ value is immeasurable. However, the deforestation statistics indicate a significant problem with trees or forest protection and conservation.
Let us battle deforestation by addressing deforestation causes, utilising effective conservation techniques, upholding sustainable land management and fostering collaborative efforts among local and international communities.
You may also partner with a professional tree arborist company for proper maintenance and professional removal of trees on your property and neighbourhood.
A well-versed and responsible team like Trees Down Under guarantees the effective and safe preservation of your trees.We adhere to environmental standards and play our part in battling deforestation in Australia. Our simple actions can go a long way. Contact Trees Down Under at any time!